Your kidneys clean your blood by removing waste and extra fluids from your bloodstream and excreting them in the form of urine. So if you’re suffering from kidney failure, your body needs help performing those functions in order to stay healthy. Kidney failure can sometimes be treated with a kidney transplant, but if that’s not an option, dialysis is another treatment that can help perform the kidneys’ functions.
Hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis are the two different forms of dialysis treatment. In this article, we’ll discuss their differences and how to choose which option is best option for you.
Hemodialysis
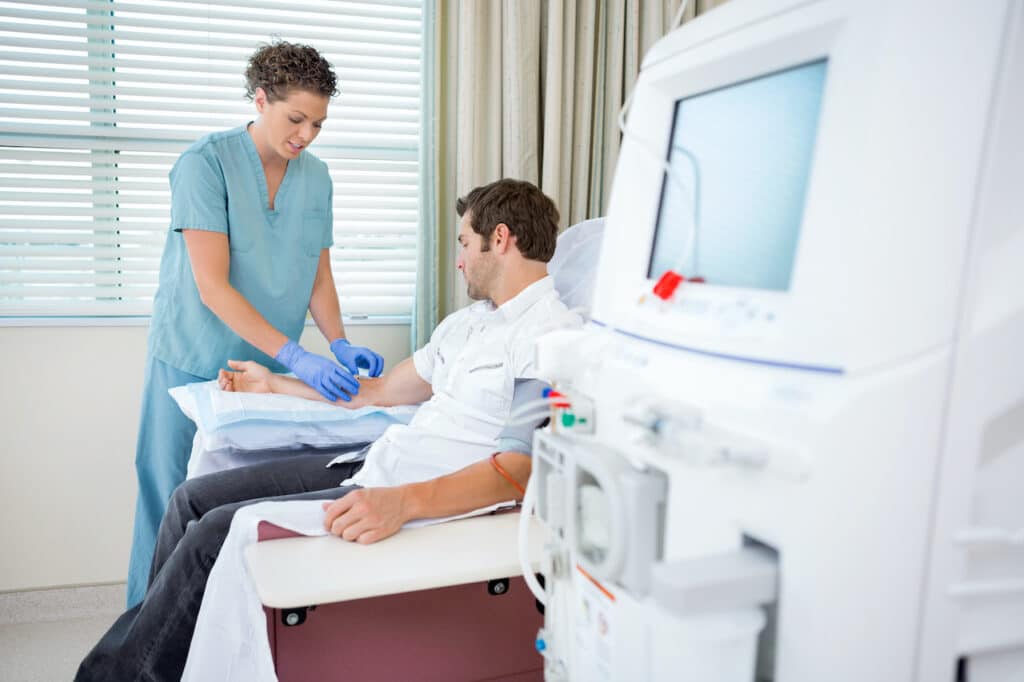
During hemodialysis, a machine is used to clean the blood with a filter called a dialyzer, which acts as an artificial kidney. Your doctor will make an access point to your blood vessels through a minor surgery on your arm or leg. The doctor may join an artery and a blood vessel together under your skin, creating a bigger blood vessel called a fistula. Or, they may insert a soft plastic tube under your skin to join an artery and a vein, creating a graft.
The doctor will connect tubes to the access point and the dialysis machine, which will then cycle your blood through the machine to be cleaned. Only a small amount of blood is out of your body at any time, as the machine continuously cycles the blood out and then back into your body.
How Does the Dialysis Machine Clean the Blood?
This dialyzer has two parts. It’s a filter, so it has one part for your blood and one for dialysate, which is a washing fluid. There is a very thin membrane that separates these parts, and the blood cells and protein stay in your blood since they are too large to pass through the membrane. The products that do pass through the membrane include urea, potassium, and creatinine. These are then washed away through the membrane, while your clean blood is returned to your body.
What Conditions Are Needed for Hemodialysis?
The good news about hemodialysis is that it can be done at home, in the hospital, or at a specialist dialysis center. You and your doctor will discuss your case’s severity and decide which is the best option for you.
Hemodialysis treatment is needed three times a week, and each appointment usually lasts between three and five hours. Those who do hemodialysis at home can do it more frequently for fewer hours at a time if they prefer. Some dietary restrictions may be required.
Advantages of Hemodialysis
- Hemodialysis only takes place three days a week in a center or a hospital, so you are free of it for four days per week
- You can choose to do it at home if your medical team agrees
- Dialysis at home allows for fewer dietary restrictions
Disadvantages of Hemodialysis
- Treatments take up several hours of your day
- Diet and fluid intake has to change and has restrictions attached to it
Peritoneal Dialysis
Peritoneal dialysis uses a different procedure to replace the kidneys’ function. Instead of using a machine to filter and clean your blood, blood is cleaned inside the patient’s abdomen.
Patients need a catheter—a soft plastic tube—placed in their belly. Dialysate fluid is passed through the catheter into the abdomen, where the lining of the abdomen acts as a natural membrane or filter to separate waste and excess fluid. Once the filtering is complete, the fluid, which retains the waste, leaves the body through the catheter.
There are two different types of peritoneal dialysis:
- CAPD: Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis. This is a continuous treatment that is machine-free. You can continue your day and go to work or school, as the sterile cleansing fluid is placed in the stomach and later drained. There is a plastic bag attached to the catheter which is used to collect and drain the used fluid containing wastes. When the exchange of fluids is done, the fluid is thrown away. This happens three to four times a day while you’re awake and only takes around half an hour to complete.
- APD: Automated Peritoneal Dialysis. This is slightly different from CAPD because there is a machine that delivers and drains out the fluid for you, and it’s done overnight. This method is often preferred by patients, since the procedure is more automated and they can just sleep through it.
Advantages of Peritoneal Dialysis
- With continuous dialysis, you can control the fluid in and out of your body more efficiently. This reduces any stress on your heart and blood vessels
- You can eat more than hemodialysis patients can
- Fewer medications are used during peritoneal dialysis
- You can go about your day with work and travel with little interruption
Disadvantages of Peritoneal Dialysis
- Some patients are not suited to peritoneal dialysis
- Weight and large abdomens can get in the way of this process being successful
- There is the complication of peritonitis, which is an infection of the abdomen, that is a possibility
- The process must be completed daily
Hemodialysis vs. Petironeal Dialysis: Choosing Your Treatment
When deciding between hemodialysis & peritoneal dialysis to choose your dialysis treatment plan, you should take your lifestyle, location, and dietary needs into account, and discuss your options with your doctor.